We will be looking at the humble audio cables and how they contribute to the seamless transmission of signals within a sound system. From connecting instruments to amplifiers and speakers, audio cables play a vital role in ensuring high-quality sound.
In this article, we will explore the different types of audio cables, their functions, and why they are essential for creating an immersive audio experience.
Unbalanced versus Balanced Cables
While cables may look similar from the outside, take a look inside and you will discover that there are differences underneath the outer cladding of the cable.
When working in live audio, you will be mainly working with analog cables that carry electrical signals. This is as opposed to digital cables that carry digital information in the form of 1s and 0s.
A cable is made up of a core and a shield. The core wire carries the signal while the shield helps to prevent noise from entering into the core. It also acts as the ground wire and the return path for the signal.
The two main types of cables that you will commonly encounter when working in audio: unbalanced and balanced cables.
What are Unbalanced Cables
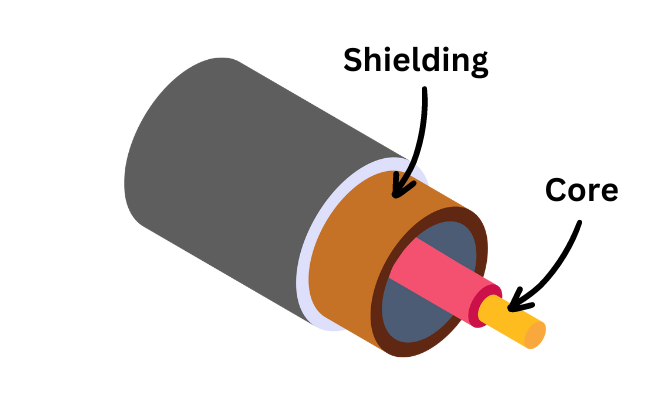
Unbalanced cables are a type of cable that carry audio signals using only two wires: a conductor wire and a ground shielding.
These cables are commonly used for shorter cable runs and in applications such as connecting guitars to amplifiers or consumer audio devices.
Unbalanced cables are more affordable and suited for simpler audio setups. However, they are also more susceptible to noise interference and can degrade signal quality over longer distances. This means that if you’re using unbalanced cables for a large sound system or an audio setup with significant cable lengths, you may experience more noise and a less clear audio signal.
What are Balanced Cables
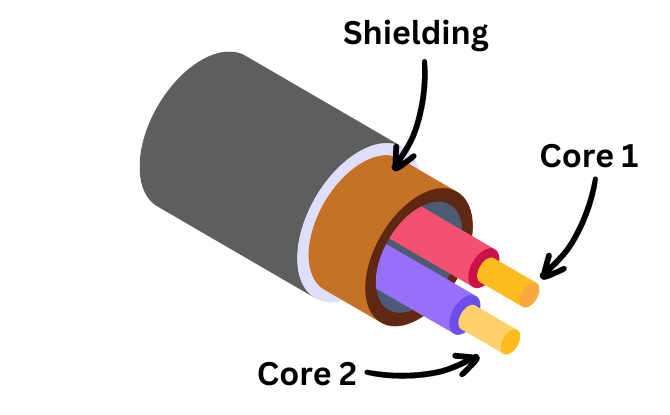
Balanced cables are designed with a ground wire and two conductor wires, allowing them to cancel out any noise or interference that may be picked up during signal transmission. This ensures that the audio signal remains balanced and free from unwanted noise, resulting in optimal audio quality.
Unlike unbalanced cables, which use only two wires, balanced cables utilize an additional wire to achieve noise cancellation. The ground wire serves as the reference point for the audio signal, while the two conductor wires carry the audio information.
Common Mode Rejection
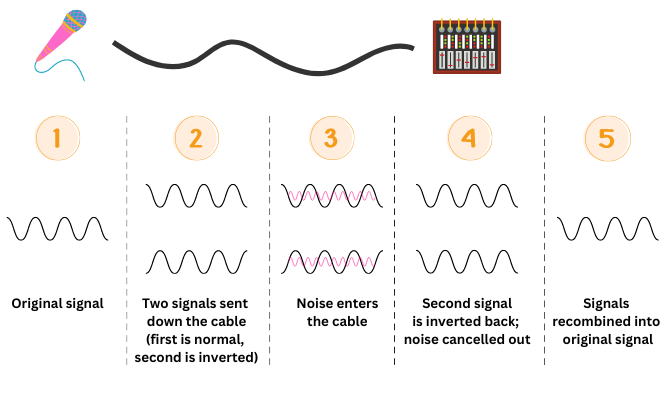
This balanced configuration helps to eliminate common-mode noise, which can be caused by external factors such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) or ground loops.
The process of noise cancellation in balanced cables involves the use of polarity inversion. As the audio signal travels through the cable, it passes through one conductor wire with the normal polarity (think of polarity as a direction) and the other conductor wire with the inverted polarity (i.e. an inverted direction).
When the signal reaches the destination device, the inverted polarity is reversed back to its original polarity, effectively cancelling out any noise that may have been picked up along the way.
This mechanism significantly reduces the chances of noise interference and ensures a clean and clear audio signal.
One of the main advantages of balanced cables, thanks to their noise cancellation capabilities, is that they can be used over longer cable runs without sacrificing audio quality.
This makes them ideal for connecting audio equipment that is far apart, such as microphones to mixers or stage monitors to amplifiers. Additionally, balanced cables are also beneficial in environments where there may be a lot of electrical noise or interference, such as in live concert venues or recording studios.
Pros & Cons of Unbalanced versus Balanced Cables
When it comes to audio cables, you have two primary options: unbalanced cables and balanced cables. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and understanding their pros and cons is crucial in determining which option is best for your audio needs.
Unbalanced Cables:
Unbalanced cables are the simpler and more cost-effective choice. They consist of two wires: a ground wire and a conductor wire. These cables are commonly used for shorter cable runs and in applications such as connecting guitars to amplifiers or consumer audio devices.
One of the main drawbacks of unbalanced cables is their susceptibility to noise interference. As the signal travels through the cable, it can pick up electrical noise, leading to a decrease in signal quality. This noise interference becomes more prominent over longer distances, impacting the overall audio experience.
Balanced Cables:
On the other hand, balanced cables provide superior noise cancellation and are ideal for longer cable runs. These cables utilize an additional wire known as the ground or shield wire. This wire is dedicated to canceling out any noise or interference picked up during signal transmission, ensuring a clean and uninterrupted audio signal.
While balanced cables offer excellent noise cancellation, they do come with some downsides. Compared to unbalanced cables, balanced cables can be more expensive. Additionally, using balanced cables requires equipment that supports balanced connections, adding to the overall cost of the audio setup.
Choosing the Right Cable:
When deciding between unbalanced and balanced cables, it’s crucial to consider your specific audio needs. If you’re working with shorter cable runs and cost-effectiveness is a priority, unbalanced cables may be the right choice for you. However, if you’re looking for superior noise cancellation and are working with longer cable runs, investing in balanced cables is the way to go.
Categorising Cables by their Connectors
At the end of cables, you will find connectors. These are connectors allow cables to be connected to equipment through input jacks located on the equipment. This allows the signal to flow out from the cables and into the equipment.
There are multiple types of connectors. Some of them are designed to work with unbalanced cables while others are used with balanced cables.
It is common to refer to cables by the type of connectors.
TS Cables
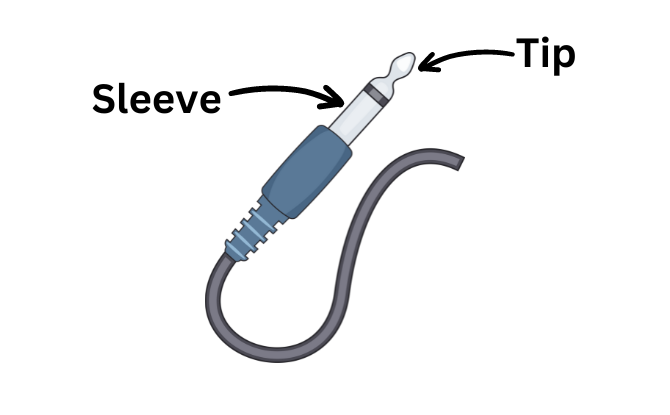
TS cables, also known as Tip/Sleeve cables, are a type of unbalanced cable that are commonly used for connecting mono sources in audio setups. Mono sources include instruments like guitars and bass, as well as effects and audio interfaces.
The Tip is connected to the core and carries the live signal. The Sleeve is connected to the shielding and acts as the return or ground path.
TS cables are typically available in 1/4″ sizes, although smaller variations like 1/8″ or 3.5mm are also available for consumer products. These cables are widely used for their simplicity and affordability, making them a popular choice.
When using TS cables, it’s important to keep the cable length as short as possible to minimize the risk of signal noise. This is especially crucial for maintaining the audio quality when connecting mono sources. By keeping the TS cables short, you can ensure a cleaner and more reliable signal transfer.
TRS Cables
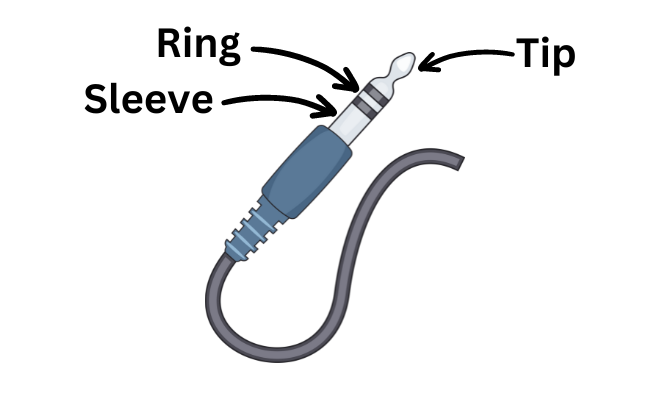
TRS cables, or Tip/Ring/Sleeve cables, are an essential tool in audio setups that require balanced connections. These cables have three contact points that allow them to be used with balanced cables. The Tip is connected to the first core, the Ring is connected to the second core and the Sleeve is connected to the shielding.
They can also be used to carry stereo audio signals (left channel, right channel and the ground).
Mixers often use TRS cables to connect auxiliary send and return channels for integrating external effects processors.
Another common application of TRS cables is in headphones. Many high-quality headphones utilize TRS connectors to ensure balanced audio delivery to each earcup, resulting in a more immersive and accurate listening experience.
XLR Cables
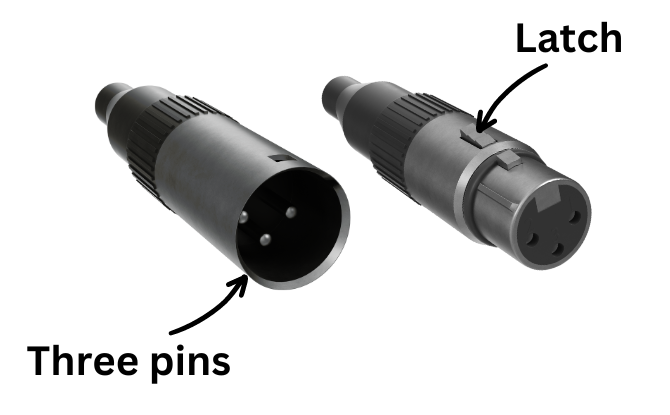
XLR cables are an integral component of professional audio setups due to their reliability and ability to deliver clean and balanced connections. The XLR connector has three pins that allow for connections to the ground wire and two conductor wires specifically designed for carrying the audio signal. The female end of an XLR connector incorporates a latch that is used keep the cables securely fasten.
The XLR cable is most commonly used with microphones. This results in them often being referred to as microphone cables.
One of the notable advantages of XLR cables is their capability to maintain a clean and high-quality signal, even over extended cable runs. This makes them particularly suitable for large-scale events or venues where a consistent audio signal is crucial. Moreover, XLR cables are known for their durability and resilience, ensuring reliable performance in demanding professional audio applications.
Speaker Cables and Speakon Connectors
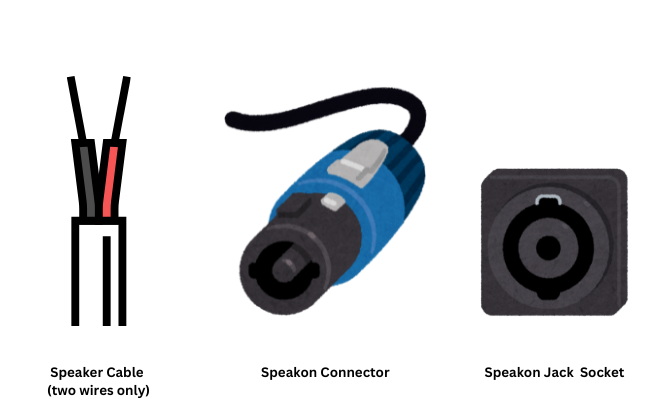

Speaker cables are designed specifically for connecting amplifiers to speakers. These cables serve the crucial role of delivering high voltage audio signals from the amplifier to the speakers with optimal efficiency and power transfer.
One common type of connector used in speaker cables is the Speakon connector. This particular connector offers a secure and locking connection, ensuring that there are no accidental disconnections during live performances or in high-demand audio environments.
It has a built-in latch and is secured into the Speakon jack by inserting and twisting to the right until the latch engages. To remove it from the jack, pull back on the latch and twist to the left and then pull ou.
Another type of connector used with speaker cables is the TS connector. This makes a speaker cable with TS connector look very similar to instrument cables. However, speaker cables will typically have a larger gauge of wire to handle the higher voltage.
RCA Cables
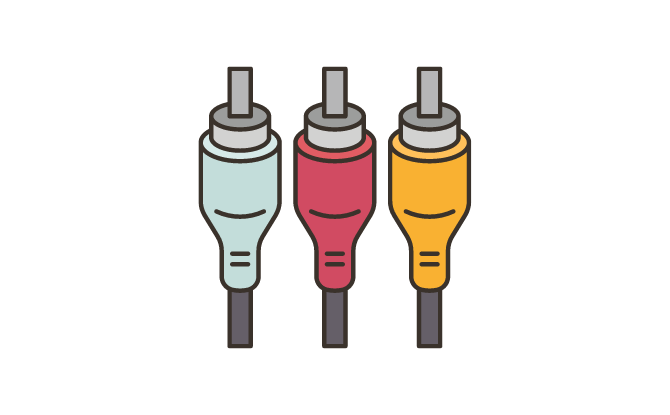
RCA cables are a popular choice for connecting audio devices in consumer audio setups and DJ systems. The RCA connector is connected to unbalanced TS cables. They are known for their distinctive red and white color-coded connectors, making them easy to identify and connect. You may also come across RCA connectors with a third yellow color connector. This is used to carry a video signal in appliances such as DVD players. Whether you’re setting up a home entertainment system or working as a DJ, RCA cables are a versatile option for transmitting audio signals.
One common use for RCA cables is connecting mixers, turntables, and CD players to mixers. With their RCA connectors, these cables enable you to seamlessly transmit audio between different audio devices. They are widely compatible and can be easily inserted into RCA jacks found on a variety of devices.
Key Takeaways
- Audio cables are crucial for transmitting signals within a sound system and ensuring accurate and efficient audio information transfer.
- Unbalanced cables are commonly used for shorter cable runs such as connecting guitars to amplifiers, while balanced cables provide superior noise cancellation and are ideal for professional audio settings.
- TS cables are used for mono sources such as guitars, while TRS cables are versatile and can be used for applications such as balanced cables or stereo connections.
- XLR cables are widely used in professional audio setups for their durability and ability to provide a clean and balanced signal transmission. They are also often referred to as microphone cables.
- Speaker cables are designed for connecting amplifiers to speakers in professional sound systems, ensuring efficient power transfer and secure connections. Speakon connectors are often used with speaker cables.
- RCA cables are popular in consumer audio setups and DJ systems and are commonly used to connect mixers, turntables, and CD players to mixers.