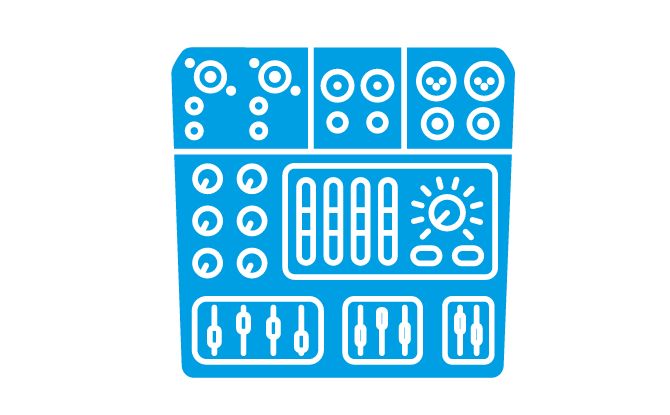
An audio mixer, also known as a mixing console, is an essential electronic device for achieving optimal sound quality in various audio productions, including music, podcasts, and live events. It plays a vital role in the seamless integration and balance of different audio signals from sources like microphones, instruments, and pre-recorded audio.
The primary function of an audio mixer is to adjust and combine these audio signals to create a harmonious blend. By fine-tuning the sound levels and applying various processing techniques, the mixer enhances the overall sound quality, ensuring a seamless listening experience for the audience.
It allows you to control the individual inputs, adjust the audio levels and processing, and route the mixed signals to multiple outputs, such as sound systems, speakers, or recording devices, according to your specific production needs.
Let’s explore audio mixers and discover how they are used in live sound.
Accept Multiple Inputs
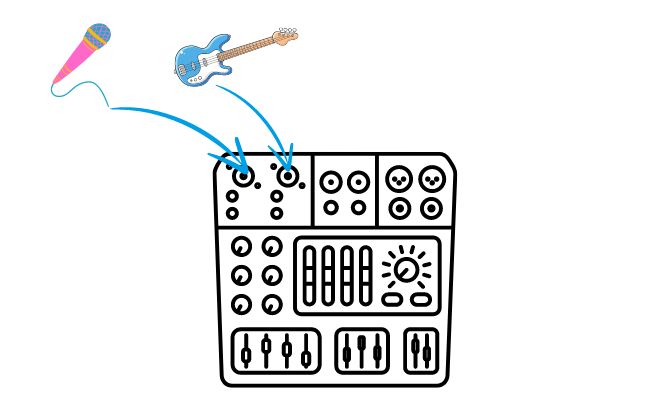
An audio mixer is designed to accept multiple inputs from various audio sources, including microphones, instruments, and synthesizers. This versatile capability allows for the simultaneous connection and control of multiple audio sources in either a live or recording situation. It can combine the various input signals into a single output signal.
Adjust the Inputs Level & Processing
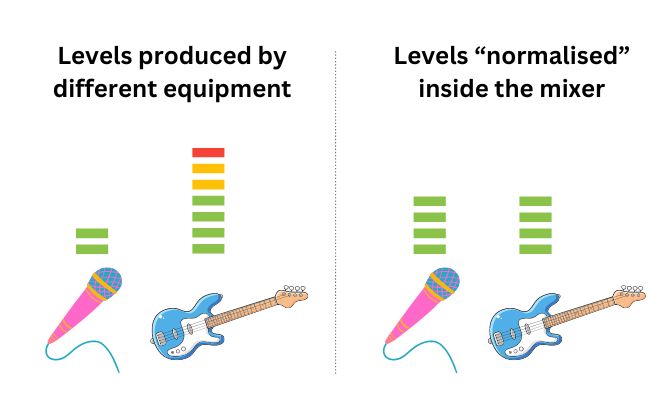
Input signals can come from equipment like microphones, instruments, music players or synthesizers. Not every input signal is the same. Some are very soft (low level) while other maybe very loud or “hot” (high level). Left on their own, the loud signals will naturally overwhelm or crowd out the softer signals.
An audio mixer has the capability to adjust the input levels for each audio source. This allows the incoming sounds to be taken into the mixer at a more uniform level. Then it would then be possible for the sound operator to determine which ones to make louder or softer in the final mix.
By adjusting the input levels, you can prevent distortion and achieve the desired volume for each source.
In addition to input level control, an audio mixer offers various processing features to enhance the audio signals. One of the essential tools is the EQ (equalization), which allows you to adjust the tonal balance of individual audio sources. With EQ knobs or sliders, you can boost or cut specific frequencies, shaping the sound to fit your preferences. This enables you to emphasize certain elements and create a more pleasing and cohesive mix.
Moreover, audio mixers enable you to apply effects to the audio signals, such as reverb or delay. Effects can significantly enhance the overall sound quality and add depth and character to your audio productions. By using the mixer’s built-in effects or connecting external effects units, you can experiment with different spatial effects, time-based effects, or modulation effects.
Send to Multiple Outputs
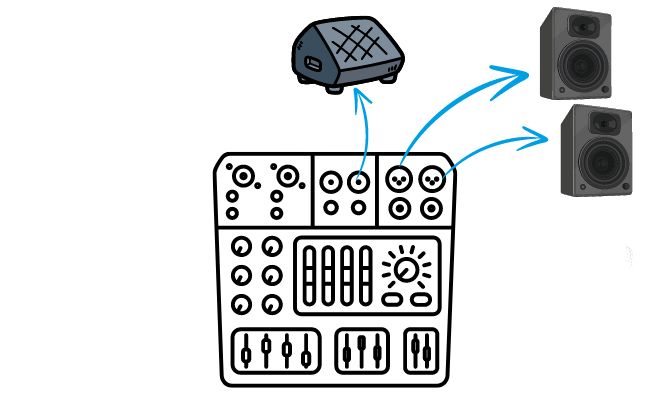
An audio mixer also allows you to send the mixed audio signals to multiple outputs, offering flexibility in routing the sound according to your specific needs.
This feature is particularly valuable for various audio situations including live events and music recording.
By utilizing the multiple outputs of an audio mixer, you can easily send the mixed audio to different destinations simultaneously. For instance, you can connect the mixer to a sound system to amplify the audio for a live audience, while also sending the signals to speakers for on-stage monitoring. Or, if you’re recording the audio, the mixer can send the mixed signals directly to a recording device, ensuring high-quality and accurate capture of the sound.
Buses Let Signals Move Around the Mixer
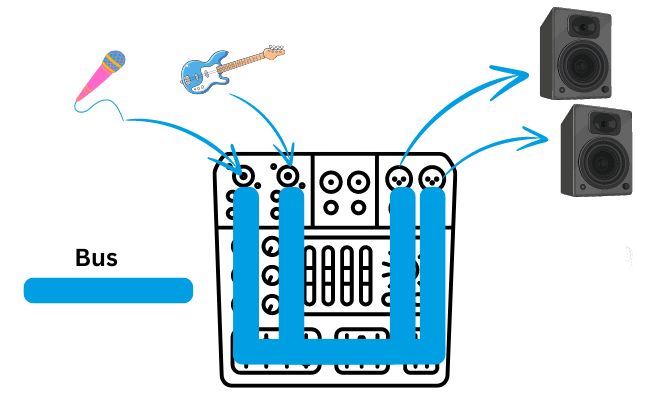
So how does the signal move around the mixer and travel from the inputs to the outputs? That’s where the buses come in.
Just like how cables are used to transmit electrical signals from equipment to equipment in a sound system, buses perform the same role but within the confines of a mixer. They are the “roads” that electrical signals use to move around inside a mixer.
You may hear about different types of buses in a mixer but they all do the same time – move sound from one part of mixer to another.
For example, you may hear about the stereo output buses. This is the route where the signals are sent out of the mixer’s main stereo out.
Another type of mixer bus is the auxiliary bus. Auxiliary buses are used for sending audio signals out of the auxiliary outputs to effects processors or for monitoring purposes. They provide a way to apply effects to specific audio signals without affecting the overall mix.
Key Takeaways: Purpose of a Mixer
- A mixer is able to accept and combine multiple input sources
- It has the ability to adjust the input sources to acceptable levels
- The signals can be sent to multiple outputs
- Within the mixer, buses are the “roads” that signals use to get around