Frequency is one of the most important concepts in sound. It is the basic building blocks of sound engineering – the alphabets of sound.
In this article, we’ll explore what is frequencies and what it means for sound waves to have different frequencies, and how frequencies are related to our perception of music.
What is Frequency?
Sound waves are generated by vibrations in the air or other media like water or solids.
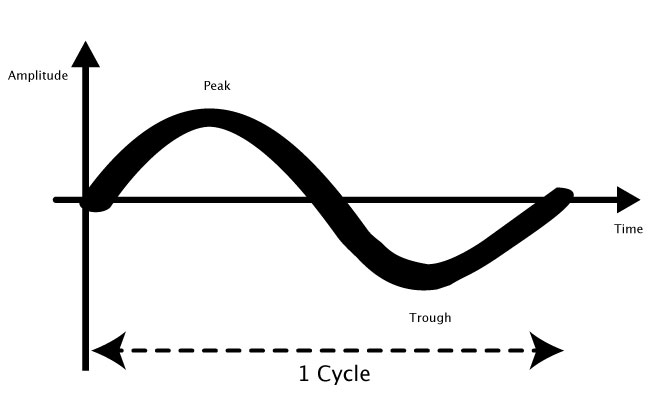
The simplest example of a sound wave is a sine wave, shown above.
Sound waves move in cycles. One cycle will have one peak and one trough.
Frequency is the number of cycles that a wave completes in one second.
What is Hertz?
The unit of measurement for frequencies is Hertz (Hz) or number of cycles per second. It measures the number of times a wave repeats itself in one second.
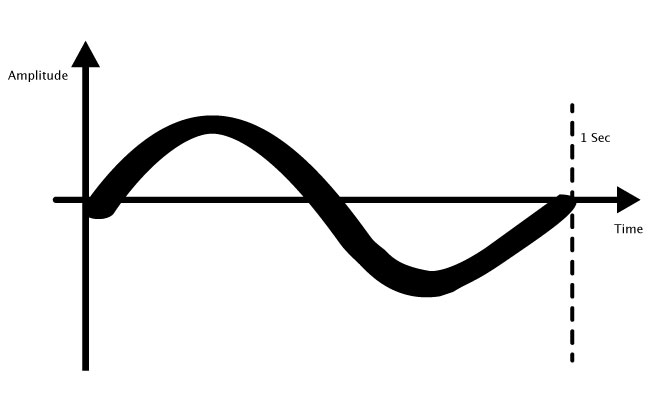
If a sound wave repeats itself one time each second, it would have a frequency of 1 Hz.
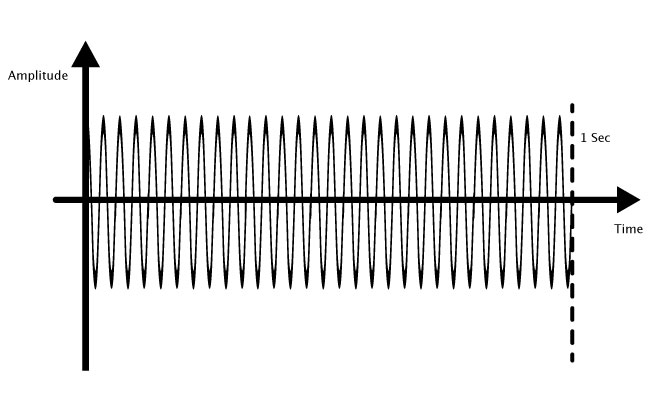
If a sound wave repeats itself 30 times every second, its frequency would be 30 Hz.
Listen to a 30 Hz sine wave. You will have to listen very closely because it a very low frequency and will sound more like a rumble. If you are using headphones, keep the volume low to avoid hearing damage.
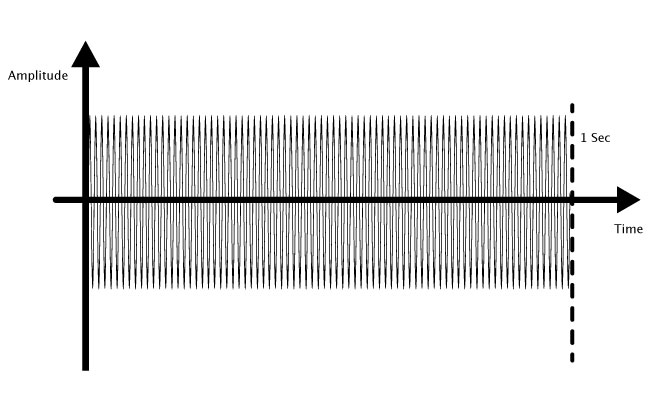

If a sound wave repeats itself 80 times a second, it would be a 80 Hz sound wave.
Listen to a 80 Hz sine wave. If you are using headphones, keep the volume low to avoid hearing damage.
Once the frequency gets to 1,000 Hz, it often shorted with the letter “k”. For example, 1000 Hz is the same as 1 kHz.
Listen to a 1 kHz sine wave. If you are using headphones, keep the volume low to avoid hearing damage.
5,600 Hz would be 5.6 kHz.
Listen to a 5.6 kHz sine wave. If you are using headphones, keep the volume low to avoid hearing damage.
Frequencies that Humans can Hear
The human ear can can hear frequencies that are between 20 Hz and 20,000 Hz (20 kHz ). Anything that is below 20 Hz or above 20 kHz is inaudible to humans.
It should also be noted that as a person grows older, he or she will start to lose his or her ability to hear higher frequency sounds.
How Do Frequencies Relate to Music?
Frequency is closely related to pitch. Higher frequency sounds are higher pitched. A super-shrill sound like a whistle has a very high frequency.
On the other hand, low frequency sounds can come across as more rumbly and deep sounding.
Musical notes are tied to specific frequencies. One frequency that musicians would be familiar with is A440. This is often used as a standard reference point for instruments to tune to. It is the pitch of of the musical note A above Middle C and has a frequency of 440 Hz.
Listen to a 440 kHz sine wave. If you are using headphones, keep the volume low to avoid hearing damage.
Other musical notes have different frequencies. The frequency of Middle C on a 88-key piano is 262 Hz. The lowest note on the piano is an A and has a frequency of 27 Hz. The highest note on the piano is a C and has a frequency of 4186 Hz.
Measuring Frequency
If you have a digital tuner or have spectrum analyzer downloaded onto your smart phone, you can view the frequencies visually.
Summary
Frequency is the number of complete cycles per second a sound wave makes. It’s measured in Hertz (Hz).
Frequency is closely related to pitch, because human ears can perceive certain frequencies as being higher or lower than others.
Next, you can learn about amplitude.

